Living with Type 1 diabetes presents its own unique set of challenges, from constant blood sugar monitoring to managing insulin levels. Amidst the daily demands of this chronic condition, it’s essential for individuals with Type 1 diabetes to secure their financial future.
This article delves into the world of life insurance specifically tailored for Type 1 diabetics. By exploring the options available, discussing the factors that affect eligibility, and providing practical tips, this article aims to empower individuals with Type 1 diabetes to navigate the process of obtaining life insurance and ensure their loved ones are protected.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
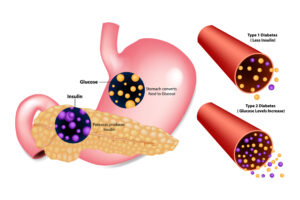
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the inability of the pancreas to produce insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. Without insulin, glucose cannot enter the body’s cells, leading to high blood sugar levels, which can cause various health complications.
Causes:
The exact cause of Type 1 diabetes is not yet fully understood. However, it is believed to be a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. Certain genes may increase the likelihood of developing the condition, while environmental factors, such as viral infections or exposure to certain toxins, may trigger the immune system to attack the insulin-producing cells.
Symptoms:
The onset of Type 1 diabetes is usually sudden and marked by the following symptoms:
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Increased hunger
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Irritability and mood changes
If left untreated, these symptoms can escalate and lead to a life-threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), characterized by a dangerous buildup of ketones in the blood.
Treatment:
The primary treatment for Type 1 diabetes is insulin therapy. Since the body can no longer produce insulin, it must be supplemented through injections or the use of an insulin pump. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial, and individuals with Type 1 diabetes often need to make dietary adjustments, engage in regular physical activity, and take oral medications to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Worst-Case Scenario:
While advancements in diabetes management have greatly improved the outlook for individuals with Type 1 diabetes, it’s important to understand the potential worst-case scenarios. Poorly controlled blood sugar levels over time can lead to severe complications, including:
- Diabetic retinopathy: damage to the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision loss or blindness.
- Diabetic neuropathy: nerve damage resulting in tingling, numbness, or pain, typically affecting the feet and legs.
- Kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy): damage to the kidneys, potentially leading to kidney failure.
- Cardiovascular disease: an increased risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and stroke.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA): a life-threatening condition characterized by a severe imbalance of blood acids and dehydration.
It’s worth noting that while these complications can be serious, proactive management, diligent self-care, and adherence to treatment plans can significantly reduce the risk and severity of such outcomes.
Impact on One’s Life Insurance Application
When applying for life insurance with Type 1 diabetes, the impact on the application process can vary depending on several factors. While individuals with well-managed Type 1 diabetes may still qualify for coverage, it’s important to understand that the process may present some challenges. Here are some key points to consider:
- Substandard or Table Rated Policies: In certain cases, applicants with well-managed Type 1 diabetes may qualify for a substandard or table rated policy. These policies typically come with higher premiums due to the increased risk associated with the condition. However, it’s worth noting that eligibility and rating decisions can vary between insurance companies.
- Automatic Denial: Unfortunately, some life insurance companies may automatically deny coverage to anyone with Type 1 diabetes, regardless of how well the condition is managed. This can be due to company-specific underwriting guidelines or risk assessment policies. It’s crucial to research and work with insurance companies that are more open to considering individuals with chronic conditions.
- Age and Tobacco Use: Younger applicants with Type 1 diabetes tend to have a higher chance of approval for life insurance coverage. This is because they typically have fewer complications and longer life expectancy. Additionally, insurance companies generally have stricter criteria for smokers, so maintaining a tobacco-free lifestyle can improve the chances of approval.
It’s essential to work with an experienced insurance agent or broker who understands the nuances of underwriting for Type 1 diabetes. They can help navigate the application process, identify insurance providers that are more likely to offer coverage, and ensure that the applicant’s medical information is accurately presented to maximize the chances of approval.
Additionally, while obtaining traditional coverage may pose challenges, there may be alternative options to explore. Guaranteed-issue life insurance policies, which do not require medical underwriting, may be available for individuals with Type 1 diabetes. However, these policies often have limitations, such as lower coverage amounts and higher premiums.
Factors that will be considered
When evaluating an individual’s life insurance application with Type 1 diabetes, several factors are typically considered by insurance companies. These factors help assess the overall risk associated with the condition and determine eligibility and premium rates. Here are some key factors that insurers may take into account:
- Age of Diagnosis and Duration: The age at which Type 1 diabetes was diagnosed and the duration of the condition are significant factors. Individuals who were diagnosed at a younger age and have had the condition for a longer period may face more challenges in obtaining coverage, as they may have a higher likelihood of complications.
- Blood Sugar Control and HbA1c Levels: Insurance companies typically review an applicant’s blood sugar control, as reflected in their HbA1c levels. Lower and well-managed HbA1c levels indicate better overall control of diabetes and may improve the chances of approval and favorable premium rates.
- Presence of Complications or Comorbidities: The existence of diabetes-related complications, such as diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, or kidney disease, can impact the underwriting decision. Insurance companies may assess the severity of these complications and their potential impact on the individual’s health and life expectancy.
- Treatment Methods and Adherence: The type of treatment being used and the individual’s adherence to medical advice are crucial considerations. Insurers may inquire about the use of insulin therapy, frequency of blood sugar monitoring, and compliance with prescribed medications and lifestyle recommendations.
- Lifestyle Choices and Overall Health: Insurance companies may also evaluate an applicant’s overall health and lifestyle choices. Factors such as weight, smoking habits, exercise routines, and any other comorbidities or pre-existing health conditions may be taken into account.
- Medical Records and Documentation: The applicant’s medical records, including physician notes, lab results, and treatment history, play a vital role in the underwriting process. Comprehensive and well-documented medical records can help insurance companies assess the individual’s health status more accurately.
- Family History: The presence of diabetes or other related health conditions in the applicant’s immediate family may be considered, as it can indicate a genetic predisposition to certain risks.
It’s important to note that each insurance company may have its own underwriting guidelines and risk assessment criteria. Therefore, it is advisable to work with an experienced insurance agent or broker who can provide guidance based on their knowledge of different insurers’ policies and requirements.
By considering these factors, insurance companies aim to assess the overall risk associated with Type 1 diabetes and make informed decisions regarding an applicant’s life insurance coverage, premium rates, and policy terms.
What does “well-managed” diabetes look like?
“Well managed” diabetes refers to a state in which an individual effectively controls their blood sugar levels and maintains good overall health. Here are some key indicators of well-managed diabetes:
- Consistent Blood Sugar Control: Well-managed diabetes involves consistently maintaining blood sugar levels within a target range. This typically means avoiding significant fluctuations and keeping both fasting and postprandial (after-meal) blood sugar levels in a healthy range.
- Target HbA1c Levels: Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a measure of average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. Well-managed diabetes usually entails achieving HbA1c levels that align with medical guidelines or individualized targets set by healthcare providers. The specific target may vary depending on factors such as age, overall health, and personal circumstances.
- Regular Monitoring: Individuals with well-managed diabetes often monitor their blood sugar levels regularly using glucose meters or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. Regular monitoring allows for timely adjustments to medication, diet, or physical activity to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
- Medication and Insulin Adherence: Well-managed diabetes involves adhering to prescribed medication regimens, including insulin injections or other medications to regulate blood sugar. Following the prescribed dosages, schedules, and administration methods demonstrates commitment to treatment and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Individuals with well-managed diabetes often adopt and maintain a healthy lifestyle. This includes following a balanced diet that focuses on whole, nutrient-dense foods and monitoring carbohydrate intake to manage blood sugar. Regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises and strength training, is also encouraged as it can aid in blood sugar control.
- Regular Healthcare Visits: Regular visits to healthcare providers, such as endocrinologists or diabetes educators, are essential for individuals with well-managed diabetes. These visits help monitor overall health, review blood sugar management strategies, and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Absence of Diabetes-related Complications: Well-managed diabetes involves minimizing the risk and progression of complications associated with the condition. This includes actively working to prevent or manage complications such as retinopathy (eye damage), neuropathy (nerve damage), kidney disease, and cardiovascular complications.
It’s important to note that achieving and maintaining well-managed diabetes requires ongoing commitment, self-care, and collaboration with healthcare providers. Each individual’s diabetes management may vary based on factors such as age, overall health, and personal circumstances. Regular communication with healthcare professionals can help establish personalized targets and strategies for optimal diabetes management.
What is a healthy AIC level for a type 1 Diabetic?
For individuals with Type 1 diabetes, a healthy A1C level typically falls within the range recommended by medical guidelines. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) suggests the following A1C targets for most non-pregnant adults with Type 1 diabetes:
- ADA Recommended Target: An A1C level of less than 7% is generally recommended for adults with Type 1 diabetes. This target aims to balance blood sugar control while minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
- Individualized Targets: It’s important to note that individualized A1C targets may be established based on factors such as age, overall health, presence of complications, and personal preferences. Some individuals, particularly those with a history of severe hypoglycemia or other health conditions, may have slightly higher targets to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate A1C target for your specific circumstances. They will consider your overall health, risk of complications, lifestyle, and treatment plan when establishing an individualized target.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, in addition to A1C testing, is also essential to ensure optimal diabetes management. Frequent communication with your healthcare provider will help track progress, make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan, and maintain good blood sugar control over time.
Tips to improve One’s chances of being approved for coverage
Improving your chances of being approved for life insurance coverage with Type 1 diabetes involves taking proactive steps to demonstrate your commitment to managing the condition and minimizing associated risks. Here are some tips to help improve your chances of obtaining coverage:
- Maintain Optimal Blood Sugar Control: Consistently managing your blood sugar levels and achieving target HbA1c levels can positively impact your application. Regularly monitor your blood sugar, follow your healthcare provider’s treatment plan, and make any necessary adjustments to maintain stable control.
- Adhere to Medical Advice: Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding medication, insulin therapy, dietary guidelines, and exercise routines. Adherence to medical advice showcases your commitment to managing the condition and can positively influence the underwriting decision.
- Lead a Healthy Lifestyle: Engaging in a healthy lifestyle demonstrates responsibility and can improve your chances of approval. Maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and avoid smoking or tobacco use. Demonstrating a commitment to overall well-being can help mitigate potential risk factors associated with Type 1 diabetes.
- Keep Detailed Medical Records: Maintain comprehensive and up-to-date medical records that accurately reflect your condition, treatment history, and overall health. Having thorough documentation can provide insurers with a clear understanding of your management efforts and improve the accuracy of the underwriting process.
- Work with an Experienced Insurance Agent or Broker: Seek guidance from an insurance professional who specializes in working with individuals with chronic conditions. They can help navigate the complexities of the underwriting process, understand the specific requirements of different insurance companies, and identify providers that are more open to covering individuals with Type 1 diabetes.
- Consider Specialized Insurance Providers or Associations: Explore insurance companies or associations that specialize in providing coverage for individuals with chronic conditions. These entities may have a better understanding of the unique circumstances surrounding Type 1 diabetes and may offer more favorable terms or coverage options.
- Be Prepared for Medical Underwriting: Understand that the life insurance application process typically involves medical underwriting, which may include a review of medical records, a health questionnaire, and potentially a medical examination. Be prepared to provide detailed information and answer questions honestly to ensure an accurate assessment of your condition.
By implementing these tips, you can demonstrate your commitment to managing Type 1 diabetes and improve your chances of being approved for life insurance coverage. While approval may still vary among insurance companies, taking proactive steps to showcase your dedication to your health can positively influence the underwriting decision.
Final thoughts…
Obtaining life insurance coverage with Type 1 diabetes may present certain challenges, but with proactive management, adherence to treatment plans, and a commitment to overall health, individuals can improve their chances of approval. Demonstrating well-managed diabetes through consistent blood sugar control, target HbA1c levels, medication adherence, healthy lifestyle choices, regular healthcare visits, and the absence of complications can positively influence the underwriting decision.
Working with an experienced insurance professional who understands the intricacies of Type 1 diabetes and collaborating closely with healthcare providers can further enhance the likelihood of securing the desired life insurance coverage.
Remember, while the process may require extra effort, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can still protect their loved ones’ financial future through appropriate life insurance planning.