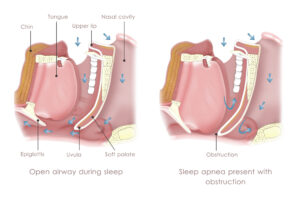
Sleep apnea is a common yet often underdiagnosed sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by interrupted breathing patterns during sleep, sleep apnea can have significant implications for an individual’s health. However, for those living with sleep apnea, obtaining life insurance can be a daunting task.
In this article, we delve into the world of life insurance and explore the challenges and strategies for individuals with sleep apnea to secure adequate coverage. By shedding light on this important topic, we aim to empower individuals with sleep apnea to navigate the insurance landscape and prioritize their financial security for a healthier future.
Understanding Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These interruptions, called apneas, can last for several seconds and occur multiple times throughout the night. The most common type of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which happens when the muscles in the throat relax and obstruct the airway.
Types of Sleep Apnea:
There are three primary types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common type of sleep apnea. It occurs when the muscles in the back of the throat relax, causing the airway to become partially or completely blocked. The blockage leads to pauses in breathing, known as apneas, and subsequent disruptions in sleep. OSA is often associated with loud snoring.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): Central sleep apnea is less common and occurs when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing during sleep. Unlike OSA, there is no physical blockage in the airway. Instead, the lack of respiratory effort causes breathing to stop temporarily. CSA is often associated with underlying medical conditions such as heart failure, stroke, or certain neurological disorders.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome (CompSA): Also referred to as mixed sleep apnea, CompSA is a combination of both obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea. Initially, it may appear as OSA, but with the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, central sleep apnea emerges or worsens. The exact cause of CompSA is not fully understood.
It’s worth noting that the distinction between the different types of sleep apnea is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment approach. A proper diagnosis through a sleep study or polysomnography can help identify the type and severity of sleep apnea in an individual, enabling healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans accordingly.
Causes:
The causes of sleep apnea can vary. In the case of OSA, factors such as obesity, excessive weight gain, anatomical abnormalities in the airway, or a family history of the condition can contribute to its development. Central sleep apnea (CSA) is less common and occurs when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing during sleep. Complex sleep apnea syndrome (CompSA) is a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea.
Symptoms:
Individuals with sleep apnea may experience a range of symptoms, including loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, abrupt awakenings accompanied by a choking sensation, morning headaches, excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and overall well-being.
To assess the severity of sleep apnea and its impact on an individual, healthcare professionals often use a sleep score, such as the Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI). The AHI measures the number of apneas and hypopneas (partial blockages of the airway) per hour of sleep. Based on the AHI score, sleep apnea can be categorized as mild, moderate, or severe.
Sleep Apnea scores:
Sleep apnea scores are measurements used to assess the severity of sleep apnea and guide treatment decisions. The two commonly used scoring systems for sleep apnea are the Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) and the Respiratory Disturbance Index (RDI).
- Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI): The AHI measures the average number of apneas (complete pauses in breathing) and hypopneas (partial reductions in airflow) per hour of sleep. It quantifies the frequency of breathing disruptions during sleep. The AHI score is categorized as follows:
-
- Normal: AHI less than 5 events per hour
- Mild: AHI between 5 and 14 events per hour
- Moderate: AHI between 15 and 29 events per hour
- Severe: AHI of 30 events per hour or higher
- Respiratory Disturbance Index (RDI): The RDI is similar to the AHI but includes additional respiratory events beyond apneas and hypopneas, such as respiratory effort-related arousals. The RDI provides a broader picture of respiratory disturbances during sleep. The RDI score is interpreted similarly to the AHI score.
These scoring systems help healthcare professionals assess the severity of sleep apnea and determine appropriate treatment options. A higher score indicates a greater frequency of breathing disruptions and often corresponds to more severe symptoms and health risks. However, it’s important to note that the impact of sleep apnea on an individual’s health can vary, and treatment decisions should consider other factors such as symptoms, underlying health conditions, and individual needs.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing sleep apnea typically involves a sleep study, also known as a polysomnography. This study monitors various physiological parameters during sleep, such as brain activity, eye movements, muscle activity, heart rate, and breathing patterns. It helps healthcare providers evaluate the frequency and severity of apneas and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Treatment Options:
Treatment options for sleep apnea aim to improve airflow and reduce the frequency of apneas during sleep. Lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss, regular exercise, and sleep position adjustments, may be recommended for mild cases. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is a common treatment method for moderate to severe sleep apnea. This involves wearing a mask over the nose or mouth during sleep, which delivers a constant flow of air to keep the airway open.
In some cases, oral appliances or surgical interventions may be considered. Oral appliances are custom-made devices that help keep the airway open by repositioning the jaw or tongue. Surgery may be an option for individuals with anatomical abnormalities that contribute to sleep apnea, but it is typically reserved for cases where other treatments have not been effective.
Worst-case scenario:
In the worst-case scenario, untreated or poorly managed sleep apnea can lead to severe health complications. It increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and even premature death. Additionally, sleep apnea can have a negative impact on mental health, contributing to depression, anxiety, and decreased quality of life.
Impact on One’s Life Insurance Application
When applying for life insurance with sleep apnea, the impact on the application can vary depending on the severity of the condition and any accompanying pre-existing medical conditions. Here are some considerations:
- Mild Sleep Apnea with Few or Any Major Pre-existing Medical Conditions: If an individual has a mild form of sleep apnea, with an AHI score below 15, and does not have significant pre-existing medical conditions, they may be able to qualify for a substandard (higher) rate. Insurance providers may consider the overall health and lifestyle factors of the applicant in addition to the sleep apnea diagnosis.
- Severe Sleep Apnea or Combined with Significant Pre-existing Medical Conditions: In cases where sleep apnea is severe, with an AHI score of 30 or higher, or if it is combined with other significant pre-existing medical conditions, applicants may face challenges in obtaining life insurance coverage. Insurance providers may perceive individuals with severe sleep apnea as having a higher risk for potential health complications or premature death, leading to a higher likelihood of coverage denial.
It’s important to note that each insurance provider has its own underwriting guidelines and may assess sleep apnea differently. Some insurers may specialize in providing coverage for individuals with sleep apnea and have more lenient underwriting criteria. Consulting with an insurance broker or agent who is experienced in dealing with sleep apnea cases can be helpful in finding suitable coverage options.
Disclosing sleep apnea and any other relevant medical conditions accurately and transparently is crucial during the application process. Failure to disclose this information could result in a denied claim or policy cancellation later on.
While severe sleep apnea or the presence of significant pre-existing medical conditions may pose challenges, it’s important not to lose hope. Seeking professional advice and exploring alternative insurance options, such as group life insurance through employers or guaranteed issue life insurance, can provide alternative avenues for obtaining coverage.
Factors that will be considered
When evaluating an individual’s application for life insurance with sleep apnea, insurance providers consider several factors to assess the level of risk associated with the condition. These factors may include:
- Severity of Sleep Apnea: The severity of sleep apnea, as indicated by the Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) or Respiratory Disturbance Index (RDI), is an essential consideration. Higher scores indicate more frequent breathing disruptions during sleep, which may be associated with increased health risks.
- Treatment and Compliance: Insurance providers will assess whether the applicant is receiving treatment for sleep apnea and if they are compliant with the prescribed therapy. Adherence to treatment, such as using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine consistently, can help manage symptoms and reduce associated risks.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Insurance providers may review an applicant’s overall health and any pre-existing medical conditions. Sleep apnea is often linked to other health issues, such as obesity, high blood pressure, cardiovascular diseases, or diabetes. The presence of these conditions can influence the assessment of risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or drug use, can affect an individual’s overall health and impact the evaluation of their life insurance application.
- Age and Body Mass Index (BMI): Age and BMI are factors that insurers commonly consider. Older age and higher BMI may contribute to an increased risk for sleep apnea-related complications.
- Follow-up and Monitoring: Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals, including scheduled sleep studies or consultations, demonstrates a proactive approach to managing sleep apnea and may be viewed positively by insurance providers.
It’s important to note that the specific weight assigned to each factor may vary among insurance providers. Some companies may have more lenient underwriting guidelines for sleep apnea, while others may be more conservative. Working with an experienced insurance broker or agent who understands the nuances of sleep apnea underwriting can be beneficial in finding suitable coverage options.
Tips for improving one’s chances at being approved
Improving your chances of being approved for life insurance with sleep apnea involves taking proactive steps and presenting yourself as a favorable candidate to insurance providers. Here are some tips to increase your likelihood of approval:
- Seek Treatment and Comply: It’s crucial to follow your prescribed sleep apnea treatment and demonstrate compliance with therapy. Consistently using a CPAP machine or adhering to other recommended treatments can help manage symptoms and reduce associated risks. Insurance providers appreciate individuals who take their health seriously and actively manage their condition.
- Maintain Regular Follow-ups: Schedule regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider, such as sleep specialists or pulmonologists. This demonstrates your commitment to monitoring and managing your sleep apnea effectively.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet. If you smoke, consider quitting, as smoking is associated with worsened sleep apnea symptoms and overall health risks. By maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in healthy habits, you can show insurance providers that you are taking steps to mitigate potential complications.
- Keep Medical Records Organized: Gather and organize all relevant medical records and documentation related to your sleep apnea diagnosis, treatment, and follow-ups. This ensures that you have accurate and up-to-date information readily available when completing your life insurance application.
- Work with an Experienced Insurance Professional: Seek assistance from an insurance broker or agent who specializes in working with individuals with sleep apnea. These professionals have experience navigating the underwriting process and can help you find insurers who are more lenient in their assessment of sleep apnea cases.
- Be Transparent and Accurate: When completing your life insurance application, be transparent and provide accurate information about your sleep apnea diagnosis, treatment, and any associated medical conditions. Failure to disclose relevant information can result in a denied claim or policy cancellation.
- Consider Alternative Insurance Options: If traditional life insurance policies are challenging to obtain, explore alternative options such as group life insurance through your employer or guaranteed issue life insurance. These alternatives may have less stringent underwriting criteria and could provide coverage options.
Remember, each insurance provider has its own underwriting guidelines, so the outcome may vary. Working with a knowledgeable insurance professional can significantly assist you in finding insurers who are more likely to approve your application based on your specific circumstances.
Final thoughts…
Obtaining life insurance with sleep apnea may present challenges, but there are steps you can take to improve your chances of approval. Seeking treatment, complying with therapy, and maintaining regular follow-ups demonstrate your commitment to managing your condition. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, organizing your medical records, and working with experienced insurance professionals can also make a difference. While severe sleep apnea or significant pre-existing medical conditions may impact your application, exploring alternative insurance options and remaining transparent throughout the process can help you secure the coverage you need.
Remember, each insurance provider has its own underwriting guidelines, so it’s essential to explore multiple options and seek expert guidance to find the best possible coverage for your specific situation. By taking proactive steps, you can prioritize your financial security and ensure peace of mind for yourself and your loved ones.