In this article, we will explore the challenges faced by individuals with PVD when applying for life insurance and discuss the factors that insurance companies consider when evaluating such applications. We will also provide some helpful tips to improve your chances of obtaining life insurance approval if you have been diagnosed with Peripheral Vascular Disease.
Understanding Peripheral Vascular Disease
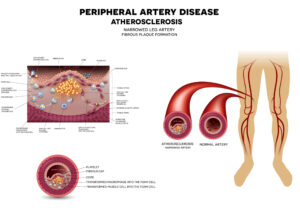
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) is a medical condition that affects the blood vessels located outside of the heart and brain. It is characterized by a narrowing or blockage of these vessels, leading to reduced blood flow to the extremities such as the legs, arms, and other peripheral areas of the body.
Causes of Peripheral Vascular Disease:
PVD is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits (plaque) build up in the arteries, causing them to narrow and become less flexible. This condition can also be influenced by other factors, including diabetes, smoking, high blood pressure, and age-related changes in the blood vessels.
Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease:
Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may be asymptomatic or present with minimal symptoms, while more advanced cases can cause significant discomfort and impair daily activities. Some common symptoms of PVD include:
- Intermittent Claudication: Pain, cramping, or fatigue in the muscles of the legs or arms during physical activity.
- Numbness or weakness in the affected limbs.
- Coldness or a pale appearance of the limbs.
- Slow-healing wounds or sores on the feet or legs.
- Hair loss or changes in the texture of the skin on the legs or feet.
- Erectile dysfunction in men.
Treatment for Peripheral Vascular Disease:
Treatment options for PVD aim to manage symptoms, slow the progression of the disease, and reduce the risk of complications. The treatment plan may include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial in managing PVD. This includes quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and following a balanced diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol.
- Medications: Medications may be prescribed to control blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels, prevent blood clots, and manage symptoms such as pain and inflammation.
- Interventional Procedures: In more severe cases, procedures such as angioplasty and stenting may be performed to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels and restore blood flow.
- Surgical Interventions: In certain situations, bypass surgery may be recommended to reroute blood flow around the blocked or narrowed arteries.
Worst-Case Scenario
In some cases, if left untreated or if the condition progresses, Peripheral Vascular Disease can lead to severe complications. The worst-case scenario may involve:
- Critical Limb Ischemia: This is a severe form of PVD characterized by severely reduced blood flow to the affected limb, resulting in tissue damage, non-healing wounds, and the potential for limb loss.
- Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Events: PVD is often associated with a higher risk of heart attacks and strokes due to the underlying atherosclerosis affecting multiple blood vessels throughout the body.
- Amputation: In extreme cases where the blood flow to a limb is severely compromised and irreversible tissue damage occurs, amputation may be necessary.
It is important to note that early detection, proper management, and adherence to treatment can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve the overall prognosis for individuals with Peripheral Vascular Disease. Regular medical check-ups and discussions with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring the condition and ensuring appropriate interventions are in place to minimize potential risks.
Impact on One’s Life Insurance Application
The impact of Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) on life insurance applications can vary depending on the severity of the condition, treatment, and lifestyle factors. Here are some general considerations:
- Mildly Treated PVD: Individuals with mild PVD who are effectively managing their condition may still be eligible for life insurance coverage. In such cases, applicants could qualify for a substandard or table rate, which means they may pay higher premiums compared to those without PVD.
- Moderate to Severe Complications: For individuals with moderate to severe complications arising from PVD, the life insurance application process becomes more complex. Insurance companies will assess applications on a case-by-case basis, taking into account factors such as the severity of the condition, medical history, treatment adherence, and overall health status. In some instances, applicants with significant complications may be denied coverage due to the higher perceived risk associated with their condition.
Nicotine or Tobacco Use: It is important to note that any applicant, regardless of how well their PVD is managed, who has used any form of nicotine or tobacco products within the last 12 months will likely be denied coverage. Smoking and tobacco use have a detrimental impact on the progression of PVD and increase the risk of complications. Insurance providers typically consider smoking as a significant risk factor and may exclude such individuals from coverage.
Factors Affecting Life Insurance Approval with PVD
Several factors significantly influence the approval process of life insurance applications for individuals with Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) including:
- Medical history and diagnosis: Insurers review medical records to understand the extent of PVD, including any related complications. The severity, duration, and stability of the condition play a role in evaluating the risks.
- Treatment and management: The type of treatment received, such as medication or surgical interventions, is considered. Adherence to prescribed treatments and regular medical check-ups show commitment to managing the disease.
- Lifestyle choices: Underwriters assess lifestyle factors like smoking, obesity, and sedentary habits that may worsen PVD. These choices can significantly impact the evaluation process and affect insurance premiums.
- Overall health status: Insurers evaluate overall health, including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and comorbidities. Maintaining good overall health can positively influence life insurance approval.
Tips for Securing Life Insurance with PVD
When seeking life insurance coverage with Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD), implementing certain tips and strategies can increase your chances of securing the desired policy. Tips and strategies such as:
- Gather comprehensive medical records: Provide insurers with complete medical records, including test results and treatment plans, to help them make an informed decision.
- Work with an experienced agent or broker: Seek assistance from professionals experienced in handling PVD cases. They can guide you through the application process, recommend suitable insurers, and negotiate on your behalf.
- Opt for a guaranteed issue or accidental death policy: These policies have fewer underwriting requirements and may be more accessible for individuals with pre-existing conditions. However, they often have lower coverage limits and higher premiums.
- Improve your overall health: Quit smoking, maintain a balanced diet, and engage in regular physical activity to demonstrate your commitment to managing PVD and overall well-being.
Conclusion…
Obtaining life insurance with PVD may present challenges, but understanding the evaluation factors and implementing appropriate measures can improve your chances of approval. By providing comprehensive medical records, working with professionals, considering specialized policies, and improving your overall health, you can navigate the life insurance application process more effectively.