Obtaining life insurance coverage is a crucial step in securing your family’s financial future. However, individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as osteoporosis, often face challenges when it comes to getting approved for life insurance. In this article, we will explore the impact of osteoporosis on life insurance approvals and provide useful tips to increase your chances of obtaining coverage.
Understanding Osteoporosis
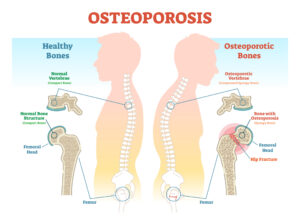
Osteoporosis is a progressive skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to an increased risk of fractures. The term “osteoporosis” translates to “porous bones,” reflecting the fragile and weakened state of the bones in individuals with this condition. It primarily affects older adults, especially postmenopausal women, but can occur in men and younger individuals as well.
Causes of Osteoporosis
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis. The primary cause is an imbalance in the process of bone remodeling, where the rate of bone breakdown exceeds the rate of bone formation. This imbalance can be influenced by various factors, including:
- Age: As individuals age, bone density naturally decreases, making them more susceptible to osteoporosis.
- Hormonal Changes: Reduced estrogen levels in women after menopause and testosterone levels in men can contribute to bone loss.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients can weaken bones.
- Lifestyle Choices: Sedentary lifestyle, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and low physical activity can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Medical Conditions and Medications: Certain conditions (such as rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, and hyperthyroidism) and medications (such as glucocorticoids) can contribute to bone loss.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
In its early stages, osteoporosis may not exhibit any noticeable symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, the following symptoms may become evident:
- Bone Fractures: Osteoporosis weakens the bones, making them more susceptible to fractures, particularly in the spine, hip, and wrist.
- Loss of Height: Multiple vertebral fractures can lead to a stooped posture and a noticeable loss of height over time.
- Back Pain: Fractured or collapsed vertebrae can cause chronic back pain, which may worsen with physical activity or movement.
- Poor Posture: Weakened bones can result in a forward curvature of the spine, leading to a rounded upper back (dowager’s hump).
Treatments for Osteoporosis
While osteoporosis is a chronic condition, several treatments can help slow down bone loss, improve bone density, and reduce the risk of fractures. The treatment approach may include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engaging in weight-bearing exercises, quitting smoking, and moderating alcohol consumption can help maintain bone health.
- Medications: Various medications, including bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), and calcitonin, may be prescribed to slow bone loss, increase bone density, and reduce fracture risk.
- Fall Prevention Strategies: Taking measures to prevent falls, such as removing hazards in the home, using assistive devices, and practicing balance exercises, can reduce the risk of fractures.
Worst-Case Scenario with Osteoporosis
In severe cases, osteoporosis can lead to debilitating complications and significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. The worst-case scenario includes:
- Multiple Fractures: Osteoporosis weakens the bones to the point where even minor accidents or minimal trauma can result in multiple fractures. These fractures can lead to chronic pain, disability, and loss of independence.
- Spinal Deformities: Progressive vertebral fractures can cause significant changes in spinal alignment, leading to kyphosis or a hunched posture. This can result in chronic pain, difficulty breathing, and decreased mobility.
- Limited Mobility: The cumulative effect of fractures and spinal deformities can severely limit an individual’s mobility. This can impact daily activities, increase dependence on others for assistance, and contribute to a sedentary lifestyle.
- Decreased Quality of Life: Chronic pain, loss of independence, and limited mobility can significantly reduce an individual’s quality of life. It may lead to social isolation, depression, and a decreased ability to engage in activities they once enjoyed.
- Increased Mortality: Osteoporotic fractures, particularly hip fractures, can be life-threatening, especially in older individuals. The complications associated with fractures, such as pneumonia, blood clots, and infections, can increase the risk of mortality.
Preventive Measures and Early Intervention
While the worst-case scenario of osteoporosis is concerning, it’s important to remember that proactive measures can help prevent or mitigate its impact. Early intervention and preventive strategies include:
- Regular Bone Density Tests: Screening for osteoporosis through bone density tests can help identify the condition in its early stages and allow for timely intervention.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a well-balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engaging in regular weight-bearing exercises, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help preserve bone health.
- Medication Compliance: If prescribed medications to manage osteoporosis, it is crucial to adhere to the treatment plan as directed by healthcare professionals.
- Fall Prevention: Implementing fall prevention measures, such as removing hazards in the home, using assistive devices, and participating in balance exercises, can reduce the risk of fractures.
- Regular Follow-ups: Scheduled check-ups with healthcare providers allow for ongoing monitoring of bone health, assessment of treatment effectiveness, and adjustments to the treatment plan if necessary.
Impact on One’s Life Insurance Application
The impact of certain health conditions on a life insurance application can vary based on the severity, complications, and overall health of the applicant. When it comes to mild cases of conditions, such as mild osteoporosis with few complications and considered a part of normal aging, preferred rates may still be possible.
However, for individuals with more severe cases of osteoporosis or significant complications, life insurance companies typically evaluate each case on an individual basis. Factors such as the extent of bone density loss, history of fractures, overall health, and management of the condition will be closely examined. In such cases, standard rates or higher premiums may be applied, reflecting the increased risk associated with the condition.
It is important to note that some insurance companies may deny coverage altogether for individuals with severe osteoporosis or other significant health complications. The decision to deny coverage is typically based on the perceived level of risk and the potential for early mortality.
However, it is worth exploring different insurance companies and working with an independent insurance agent who specializes in high-risk cases. They may have knowledge of insurance carriers that are more lenient or have specific policies tailored to individuals with pre-existing conditions.
Additionally, the availability of coverage options may also depend on the type of life insurance being sought. For instance, term life insurance policies tend to have more lenient underwriting requirements compared to permanent life insurance policies. It may be easier to secure coverage through a term life insurance policy, especially if the condition is well-managed and not severe.
Factors that will be considered
When applying for life insurance, several factors are taken into consideration by insurance companies to assess the risk associated with providing coverage. These factors help determine the premiums and coverage options that will be offered to the applicant. Here are some key factors that insurers consider during the life insurance application process:
- Age: Age is a significant factor in life insurance underwriting. Generally, younger individuals tend to receive lower premiums as they are perceived to have a longer life expectancy and lower risk of mortality.
- Health History: Insurance companies evaluate an applicant’s medical history, including pre-existing conditions, chronic illnesses, surgeries, and hospitalizations. This information helps insurers assess the potential health risks and mortality risk associated with the applicant.
- Lifestyle Choices: Lifestyle habits and behaviors play a crucial role in life insurance underwriting. Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, and participation in high-risk activities (e.g., skydiving or extreme sports) can increase the risk profile of an applicant and result in higher premiums.
- Family Medical History: Insurance companies also consider the health history of an applicant’s immediate family members, such as parents and siblings. Certain hereditary conditions or diseases in the family may impact the risk assessment for the applicant.
- Height and Weight: Body mass index (BMI) is often taken into account during the underwriting process. Applicants who fall within a healthy weight range for their height generally receive more favorable premiums compared to those who are overweight or obese.
- Occupation and Hobbies: Certain occupations and hobbies may carry higher risks. For example, individuals working in hazardous occupations like mining or firefighting may face higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of accidents or injuries. Similarly, engaging in risky hobbies such as mountain climbing or piloting small aircraft can impact the risk assessment.
- Medical Examinations: Insurance companies may require applicants to undergo a medical examination, including blood tests, urine tests, and a physical examination. These tests help evaluate overall health, identify any underlying health conditions, and assess key health indicators like cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and glucose levels.
- Coverage Amount: The amount of coverage an applicant seeks will also be considered. Higher coverage amounts may require more extensive underwriting and may result in more thorough evaluations of the applicant’s health and medical history.
It’s important to note that different insurance companies have varying underwriting guidelines and may weigh these factors differently. Therefore, it’s beneficial to work with an experienced independent insurance agent who can guide you through the application process, understand your unique circumstances, and help you find the best coverage options at competitive rates.
Conclusion…
While osteoporosis can complicate the life insurance approval process, it does not make it impossible to obtain coverage. By understanding how osteoporosis affects life insurance approvals, providing comprehensive medical documentation, adopting a healthy lifestyle, considering alternative policies, working with an independent insurance agent, and being patient and persistent, you can increase your chances of securing life insurance coverage that safeguards your family’s financial future.